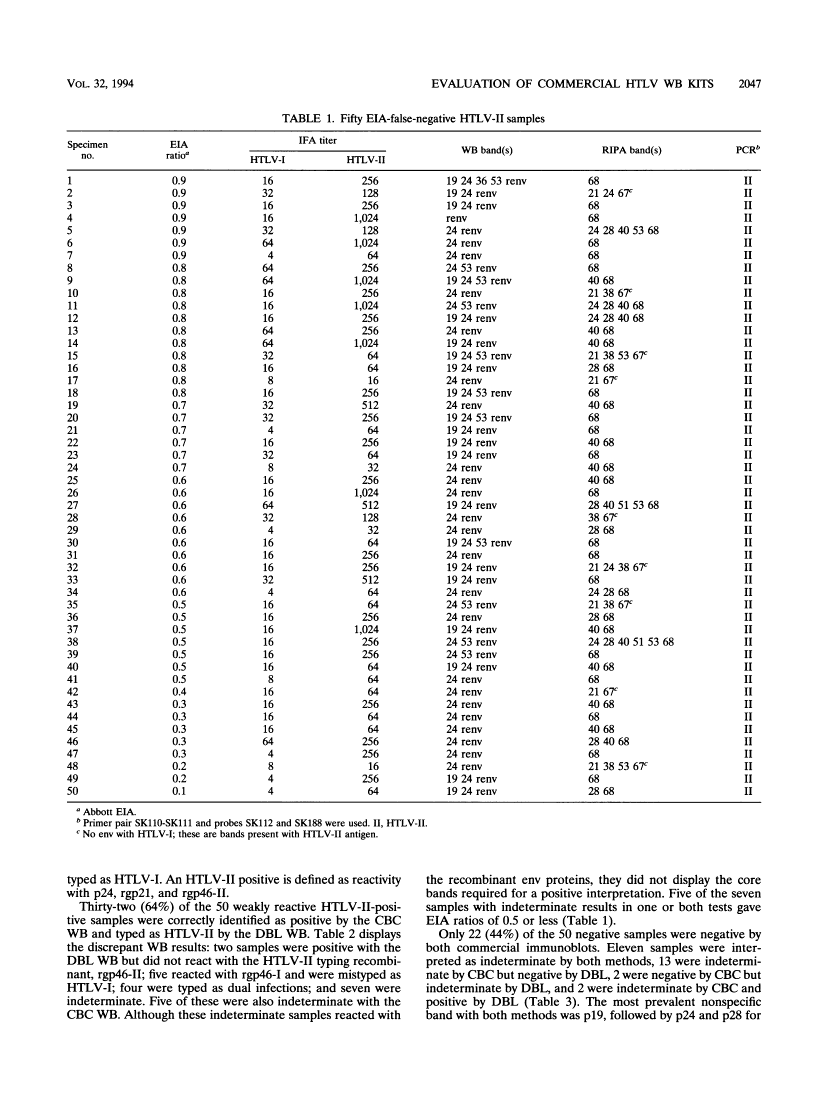
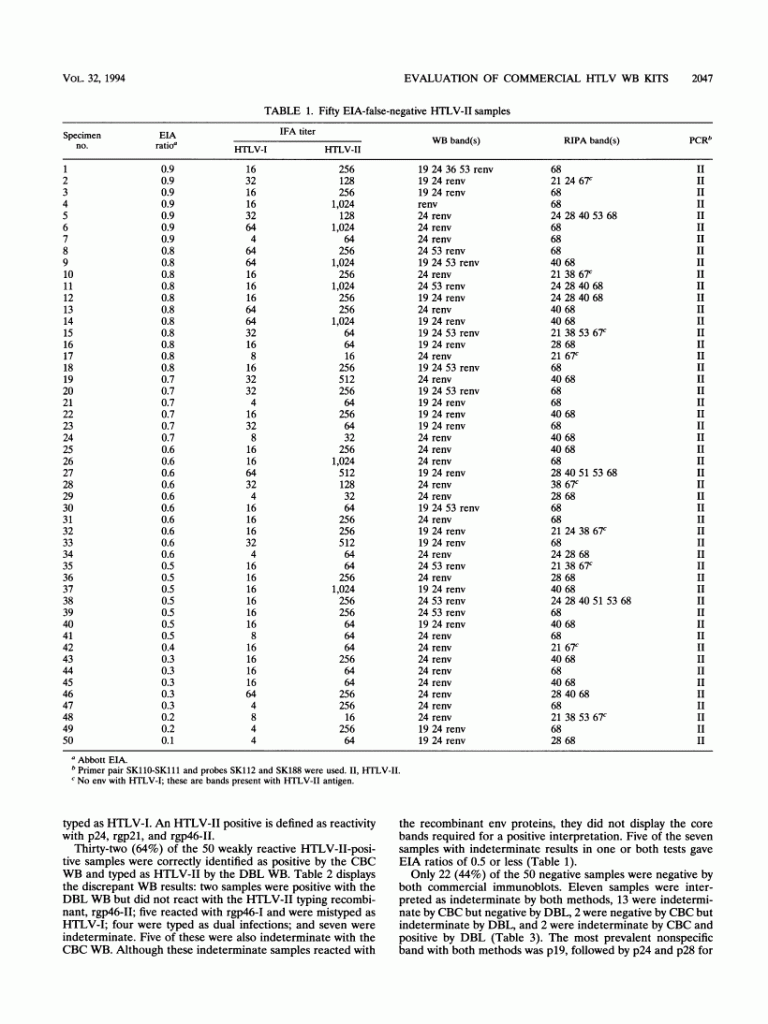
Evaluation of two commercial human T-cell lymphotropic virus western blot (immunoblot) kits with problem specimens.
We evaluated two commercial human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) Western blot (WB; immunoblot) kits, Cambridge Biotech Corp. (CBC) and Diagnostic Biotechnology Ltd. (DBL). Both strategies make use of HTLV sort I (HTLV-I) viral lysate and rgp21.
The DBL WB package additionally distinguishes between HTLV-I and HTLV-II antibodies, utilizing an HTLV-I-specific and an HTLV-II-specific recombinant. Fifty weakly reactive HTLV-II-positive plasma specimens which had been falsely adverse with the Abbott enzyme immunoassay (EIA) and 50 Ortho EIA false-positive samples had been chosen to find out sensitivity and specificity.
The sensitivities of the CBC and the DBL WB kits had been 90 and 68%, respectively. All optimistic samples reacted with rgp21 in each kits, however some didn’t show core bands. Five samples had been typed as HTLV-I and 4 had been typed as twin an infection by the DBL WB package. The specificities of the CBC and DBL kits had been 48 and 70%, respectively.
The most prevalent WB response with the adverse samples was with the core protein, p19, adopted by p24 and p28 for CBC and rgp21 and p28 for DBL. DBL had two false-positive interpretations, and CBC had none, rgp21 was probably the most delicate antigen in each kits for the weakly reactive HTLV-II samples.
If all samples not reacting with this protein had been interpreted as WB adverse, regardless of different bands, the specificity would enhance to 90% for CBC and 86% for DBL.
Evaluation of three commercial enzyme immunoassay kits for detecting faecal Clostridium difficile toxins.
The detection of faecal cytotoxicity utilizing tissue tradition was in contrast with three commercial Clostridium difficile enzyme immunoassay (EIA) kits; Premier C difficile toxin A (Meridian Diagnostic, Inc.); CD-TOX C difficile toxin A (Porton Cambridge); and Cytoclone A+B EIA (Cambridge Biotech Corporation). Of 160 faecal samples examined by all 4 strategies, 52 (32.5%) had been cytotoxic, 44 (27.5%) had been optimistic by Premier, 48 (30%) by CD-TOX EIA, and 50 (31.3%) with Cytoclone.
When in contrast with detection of cytotoxicity by tissue tradition assay, the next efficiency indices had been obtained: Premier, sensitivity 84.1%, specificity 99.1%, optimistic predictive worth (PPV) 97.8%, adverse predictive worth (NPV) 93%; CD-TOX, sensitivity 92.3%, specificity 88.0%, PPV 78.7%, NPV 95.9%; Cytoclone, sensitivity 96.2%, specificity 93.5%, PPV 87.7%, NPV 98.1%. EIA outcomes had been obtainable inside three hours, whereas the outcomes of the cytotoxin assay had been obtainable after 24-48 hours.
All three kits offered passable outcomes and, though comparatively costly, all could possibly be used within the laboratory successfully to display screen for diarrhoeal illness related with C difficile.
